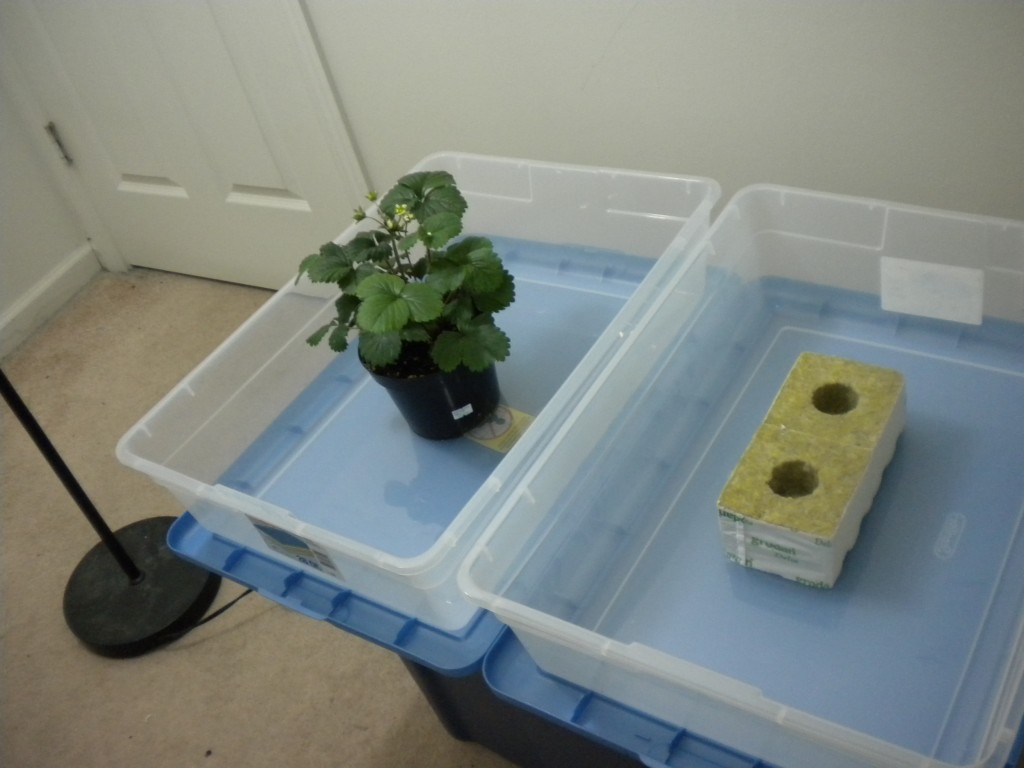
So you want to start an indoor garden but don’t know how to build a grow box. Building a grow box is actually simple once you understand the mechanics. Today you will learn every thing you need to know to build your own grow box.
The following guide will walk you through the basics of constructing a grow box out of an old piece of furniture. A lot of indoor gardeners are also very enthusiastic about recycling, so this should really hit home for a lot of you. The dresser grow box could be considered a grow cabinet, whatever you want to call it, the function is the same.
5 Reasons You Need Grow Box Plans:
1. Grow Room Ventilation: There is too much to say here. You will obviously need some sort of exhaust. The size of fan you need depends on the size of your grow box or grow room. This simple grow box uses PC fans which can be wired to an old PC power supply very easily. You can also control the timing of the fans by putting the power supply on a timer.
WARNING: Do not use the biggest power supply you can find. Stick to a smaller power supply with low wattage because the fans use very little power. If you do not know what you are doing, use a pre-made fan that you can just plug in. For 20 bucks you can get a dryer type ventilation fan that can be attached to ducting.

2. Reflective: Reflectiveness should depend on your budget. Aluminum foil is probably the cheapest material, but it certainly doesn’t reflect the most light. Since you will likely be using small grow lights, you will want to get the most out of it. White poly or Mylar are the premium choice.
3. Water proof/Bug proof/Mold proof: Water proofing is one of the most important things about building a grow box. All hydroponic systems should be in water proofed grow boxes, or outdoors where they can’t possibly make a mess. I’ll discuss bug proof more in the next point. Mold proofing takes a little common sense. Don’t use carpet for the floor of your grow box or anything dumb like that.
4. Air tight: You will want your grow box to be air tight so that light doesn’t escape, bugs will have a harder time getting in, and you will want control of the ventilation.
5. Odor control: Some people enjoy having fresh herbs, vegetables, and fruits growing in their house, but don’t want their house to smell like a garden or green house. Some people just don’t like that smell. You can get a carbon filter for the unwanted smells, but you will need to get an inline fan, which could dramatically raise the price.
Electrical Components
Please make sure all of your electrical components are away from possible water sources. You should place your outlets on the out side of the grow box and hung up. The last thing you want is water in your electrical components.
Key Components